The modern world operates on efficiency and speed. Barcode Roll is a tool that supports this need. It enables quick scanning and data collection in various industries. Retail, logistics, and healthcare rely heavily on this technology.
Barcode Roll consists of multiple barcode labels on a single roll. This design simplifies labeling processes. Workers can easily peel off the desired label and apply it. However, not all businesses use it effectively. Some still struggle with organization. This leads to delays and errors during inventory management.
Embracing Barcode Roll can improve operations significantly. Yet, implementation isn’t always flawless. Companies must train employees to use this tool correctly. Misunderstandings can result in wasted resources. Overall, Barcode Roll is a critical component in modern technology but requires thoughtful execution.
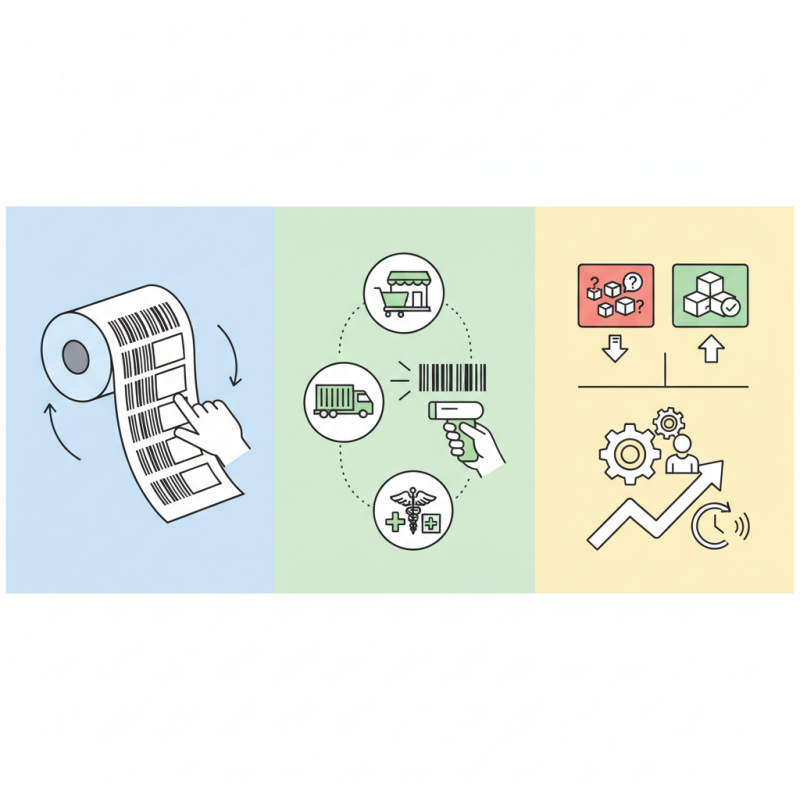
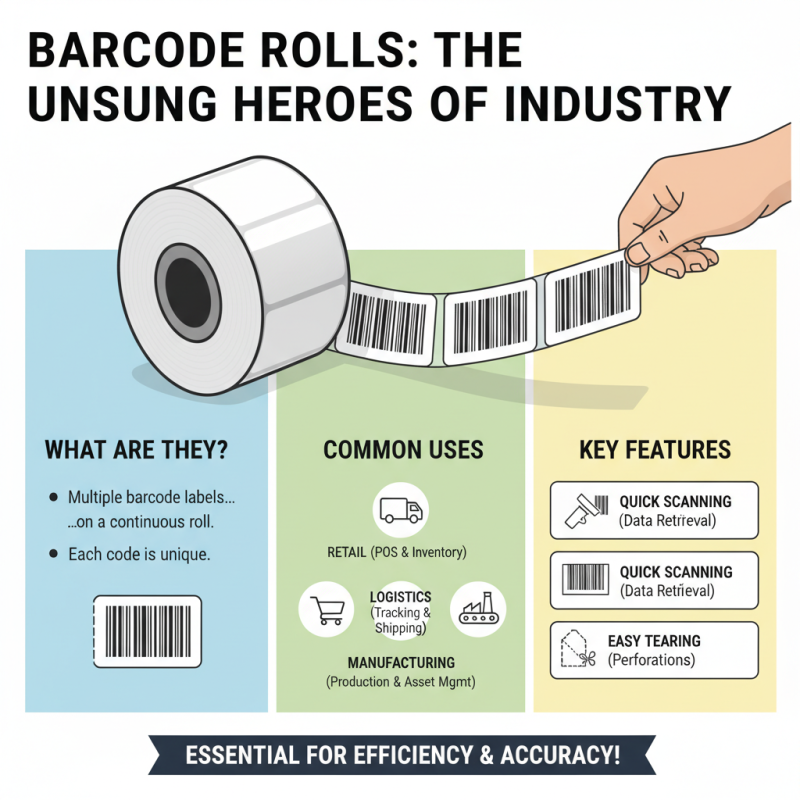
A barcode roll consists of multiple barcode labels on a roll. These rolls are used in various industries, from retail to logistics. Each barcode is unique and can be scanned for quick information retrieval. The structure usually includes a printed code alongside a blank space for easy tearing.
In practice, barcode rolls streamline operations. Workers can quickly affix labels to products as they move through the supply chain. This speed often reduces human error. However, some may find it challenging to properly align the barcodes. Misalignment can lead to scanning issues. Additionally, not all printers are compatible with every roll type.
When using barcode rolls, it is crucial to ensure the labels are of high quality. Smudged or damaged barcodes can cause delays. Users sometimes overlook the importance of regular printer maintenance. Neglecting this can result in poor print quality. These details may seem minor, but they play a significant role in efficient business practices.
Barcode technology has evolved significantly since its inception. The first barcode was scanned in 1974 on a pack of gum. This marked a turning point in retail. Prior to this, inventory tracking was slow and prone to human error. According to industry reports, the retail sector saw a 20% increase in efficiency after adopting barcodes. This shift reduced checkout times and streamlined inventory management.
By the 1980s, barcode systems expanded beyond retail. They entered the healthcare, warehousing, and manufacturing sectors. A report from a leading technology analyst stated that over 80% of organizations adopted barcode systems by the 1990s. They recognized the need for accurate tracking and data collection. However, not all implementations have been smooth. Some businesses struggled with integration into existing processes.
Today, barcode technology continues to innovate. New systems, like QR codes and 2D barcodes, offer more data capacity. Statistics suggest that 50% of consumers now engage with products using barcodes for discounts and information. Yet, reliance on technology does pose challenges. Issues like poor scanning conditions still affect accuracy. There is a growing need for organizations to continuously evaluate their barcode systems and adapt to emerging technologies. The history of barcode development reflects a journey of progress, filled with both triumphs and trials.
Barcode rolls are becoming increasingly relevant across various industries. Retail, logistics, and healthcare sectors utilize them for efficiency in tracking products. According to industry reports, the global barcode technology market is projected to reach $5.37 billion by 2027. This growth shows how essential barcode rolls have become in daily operations.
In retail, barcode rolls help streamline inventory management. Stores use them for quick scanning at checkout. This reduces wait times and enhances customer satisfaction. In logistics, barcode labels on packages ensure accurate tracking during shipments. A report by Gartner highlights that effective tracking can reduce shipping errors by over 30%.
Tip: Always check the compatibility of your barcode rolls with existing systems.
Healthcare also benefits significantly. Hospitals use barcode rolls to track medication and patient information. This minimizes human error and ensures safety. A study published in the Journal of Healthcare Management noted that barcode utilization can result in a 41% decrease in medication errors.
Tip: Regularly train staff on the latest scanning technologies.
Despite these advancements, issues can arise. Poor quality rolls may lead to scanning failures. This can cause delays and customer frustration. Ongoing improvements in barcode technology are essential for better performance.
Barcode rolls have become essential tools for modern inventory management. Their use offers numerous advantages that streamline tracking processes. According to a recent industry report, businesses utilizing barcode technology can improve stock accuracy by up to 30%. This efficiency leads to reduced labor costs and minimized errors in inventory counts.
One significant advantage of barcode rolls is their ability to enhance data collection. Scanning these rolls quickly gathers information about product quantities and locations. This real-time data enables businesses to make informed decisions swiftly. However, some companies still struggle with manual processes, risking inaccuracies. Transitioning fully to barcode technology can mitigate these issues effectively.
Barcode technology continues to evolve, shaping various sectors. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with barcodes is gaining traction. According to a recent industry report, over 72% of businesses plan to implement AI-based barcode systems by 2025. This move enhances accuracy and streamlines inventory management. As a result, companies will save valuable time, a critical factor in today's fast-paced market.
Mobile scanning is another growing trend. More users are relying on smartphones for scanning barcodes. Surveys show that 64% of consumers prefer mobile services for quick access to product information. This trend reflects a shift towards convenience. Yet, it raises questions about data security and privacy.
Tips: Make sure to regularly update your scanning apps. Outdated software can lead to vulnerabilities. Secondly, educate employees on data protection. This is crucial as barcode technology advances. Consider these factors for a smoother transition to modern barcode practices.
This bar chart illustrates the percentage of barcode technology adoption across various industries. Retail shows the highest adoption at 85%, followed by Food & Beverage and Manufacturing, reflecting the crucial role barcodes play in inventory management and sales tracking.